1.
Which Bahmani Sultan shifted his capital from Gulbarga to Bidar?
2.
How many terrestrial planets are there?
3.
The Olympic Winter Games 2026 will be held in ________.
4.
The Ravana Phadi cave and Durga Temple in Aihole depict the architectural style of which dynasty?
5.
Who succeeded Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan to the throne?
6.
In 1976, under Article 51A, in which part of the Indian Constitution were the Fundamental Duties included?
7.
Which of the following is one of the characteristics of capital goods?
8.
Kanak Rele, who founded the Nalanda Dance Research Centre, was an artist of which classical dance form of India?
9.
The Rabi season of agriculture begins in October–November and ends in ________.
10.
The red color of tomatoes is due to the presence of ________.
11.
In which part of India is a cold mountainous climate found?
12.
What is the chemical formula of sodium bicarbonate?
13.
Which of the following chemical compounds is present in turmeric?
14.
The ozone layer absorbs which type of radiation?
15.
Which of the following organizations, divided into two branches, was founded by Lokmanya Bal Gangadhar Tilak and Annie Besant?
16.
Ebony and mahogany trees are found in which type of forests?
17.
At the time of independence, what percentage of India's population was dependent on agriculture?
18.
Who is known as the inventor of the Mohan Veena in India?
19.
Which airport is known as Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose International Airport?
20.
Who among the following was not associated with the 'Moderate' phase of the Indian National Congress?
21.
Which of the following Acts was based on the Mountbatten Plan?
22.
The Great Indian Plains are mainly known for __________.
23.
The Omkareshwar Project is related to which of the following rivers?
24.
The Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve is located in which state?
25.
Under the Sagarmala Project, the overall group of projects was divided into how many pillars?
26.
In India, the highest level of seasonal unemployment is found in which sector?
27.
Which of the following is considered a capital expenditure?
28.
Which of the following cities has emerged as the electronic capital of India?
29.
Which river forms an estuary before falling into the Arabian Sea?
30.
On which date is World Blood Donor Day observed every year?
31.
Where will India’s first underwater museum be located?
32.
In which year was Guru Nanak Dev, the founder of Sikhism, born?
33.
What was the major characteristic of the Indian financial system before the enactment of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949?
34.
Who painted the 1859 artwork ‘Relief of Lucknow’?
35.
From which site of the Indus Valley Civilization was the bronze ‘Dancing Girl’ statue discovered?
36.
Which of the following is a characteristic of Indian rural settlements?
37.
Which of the following tribes is a recognized tribe in the state of Himachal Pradesh?
38.
During which Five-Year Plan was the focus shifted towards industrialization rather than agriculture?
39.
कौआ डाली से उड़ गया। इस वाक्य में कौआ शब्द का तत्सम रूप प्रयुक्त कर वाक्य पूर्ण कीजिए।
40.
निम्न में से किस वाक्य में कारक चिह्न का अशुद्ध प्रयोग हुआ है-
41.
’गृहस्थ’ का विलोम शब्द नीचे दिए विकल्पों में से चुनिए-
42.
’कृतज्ञ’ का विलोम शब्द हैं
43.
’खत पढ़ते हुए उसकी _______ लड़खड़ाने लगी थी।’ वाक्य के रिक्त स्थान के लिए विदेशी शब्द चुनकर वाक्य पूर्ण कीजिए-
44.
निम्नलिखित में से "भीक्षा" शब्द का तद्भव रूप क्या होगा?
45.
निम्नलिखित में से "सियार" शब्द का तत्सम रूप क्या है?
46.
निम्नलिखित में से "दासी" शब्द का पुल्लिंग रूप क्या होगा?
47.
'रश्मि रथी' खण्ड काव्य किसके द्वारा लिखा गया है?
48.
हरिवंश राय बच्चन द्वारा रचित निम्न में से कौन-सी पुस्तक है?
49.
निम्ननलिखित शब्दों में से उचित स्थान पर लगे अनुस्वार वाले शब्द छाटिएँ-
50.
खड़ी बोली का प्रयोग सबसे पहले किस पुस्तक में हुआ?
51.
हिन्दी भाषा किस लिपि में लिखी जाती है?
52.
निम्नलिखित में से अघोष वर्ण कौन – सा हैं?
53.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से शुद्ध रूप है
54.
हिन्दी शब्दकोश में 'क्ष‘ का क्रम किस वर्ण के बाद आता हैं?
55.
नीचे दिए गए विकल्पों में से तद्भव शब्द का चयन कीजिए
56.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से सही यौगिक शब्द को चुनिए
57.
पीताम्बर, लालफीताशाही और चारपाई शब्द निम्न में से किसके उदाहरण हैं?
58.
जिन शब्दों की उत्पत्ति का पता नहीं चलता, उन्हें कहा जाता हैं?
59.
कौन – सा विकल्प वैचारिक अन्तर के समानार्थी शब्दों का हैं?
60.
’अद्भुत’ शब्द का समानार्थी नहीं हैं
61.
किस वाक्य में सकर्मक क्रिया हैं?
62.
वाच्य कितने प्रकार के होते हैं?
63.
'उपसर्ग का प्रयोग कहाँ होता हैं?
64.
’यथास्थान‘ सामासिक शब्द का विग्रह होगा
65.
‘त्रिवेणी’ शब्द में कौन – सा समास हैं?
66.
शान्त रस का स्थायी भाव है
67.
हिन्दी साहित्य में छन्दशास्त्र की दृष्टि से पहली कृति कौन हैं?
68.
‘रघुपति राघव राजाराम’ में अलंकार हैं
69.
‘उल्का सी रानी दिशा दीप्त करती थी’ वाक्य में उपमान है उपरोक्त पंक्ति में अलंकार है
70.
निम्नलिखित गद्याशं को पढ़कर प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए-
शिक्षा मनुष्य के जीवन का वह दीपक है, जो अज्ञान रूपी अंधकार को दूर करता है और व्यक्ति को सही दिशा में आगे बढ़ने का मार्ग दिखाता है। शिक्षा केवल किताबी ज्ञान नहीं होती, बल्कि यह एक ऐसा साधन है जो व्यक्ति के व्यवहार, सोच और कार्यशैली को सकारात्मक रूप से प्रभावित करती है। प्राचीन भारत में शिक्षा को बहुत ऊँचा स्थान प्राप्त था। गुरुकुलों में विद्यार्थी केवल पाठ्यक्रम ही नहीं पढ़ते थे, बल्कि वे जीवन मूल्यों, मर्यादा, संयम और आत्मनिर्भरता का भी अभ्यास करते थे। आज भले ही शिक्षा पद्धति बदल गई हो, परंतु शिक्षा का उद्देश्य आज भी वही है — एक सच्चे, सजग, और उत्तरदायी नागरिक का निर्माण। शिक्षा व्यक्ति को आत्मविश्वास देती है। एक शिक्षित व्यक्ति समाज की समस्याओं को समझ सकता है, उनके समाधान ढूंढ सकता है और दूसरों को भी जागरूक बना सकता है। शिक्षा ही वह साधन है, जो समाज में व्याप्त रूढ़ियों, अंधविश्वासों और अन्याय के विरुद्ध आवाज़ उठाने की ताकत देता है। महात्मा गाँधी ने कहा था, “वास्तविक शिक्षा वही है जो शरीर, मन और आत्मा — तीनों का समन्वित विकास करे।” इसका तात्पर्य है कि शिक्षा केवल परीक्षा पास करने या नौकरी पाने का माध्यम न होकर एक समग्र व्यक्तित्व निर्माण की प्रक्रिया होनी चाहिए। आज के दौर में डिजिटल शिक्षा, ऑनलाइन कक्षाएं और तकनीकी माध्यमों ने पढ़ाई को आसान बना दिया है, लेकिन इसके साथ ही नैतिक शिक्षा, अनुशासन और मानवीय मूल्यों की शिक्षा भी उतनी ही आवश्यक है। यदि कोई व्यक्ति डिग्रियों से भरा हो लेकिन उसमें सहानुभूति, ईमानदारी और सेवा-भाव न हो, तो वह शिक्षित कहलाने योग्य नहीं। शिक्षा केवल स्कूल या कॉलेज तक सीमित नहीं है। जीवन भर सीखते रहना, नए अनुभवों से ज्ञान प्राप्त करना, गलतियों से सीखना — यह भी शिक्षा का ही एक रूप है। माता-पिता, शिक्षक, समाज और स्वयं जीवन — सभी शिक्षा के स्रोत हैं। एक शिक्षित समाज ही प्रगति कर सकता है। शिक्षा ही वह नींव है जिस पर एक सशक्त राष्ट्र का निर्माण होता है। इसलिए यह हम सभी का कर्तव्य है कि हम स्वयं भी शिक्षा प्राप्त करें और दूसरों को भी शिक्षित करने में सहयोग दें। विशेषकर बालिकाओं और वंचित वर्ग के बच्चों को शिक्षा का अवसर प्रदान करना समाज की सच्ची सेवा है। इस प्रकार, शिक्षा वह अमूल्य धन है जिसे कोई चुरा नहीं सकता, कोई बांध नहीं सकता और जो जितना बांटें, उतना ही बढ़ता है। यही शिक्षा की सबसे बड़ी विशेषता है।
प्रश्न 1. शिक्षा का वास्तविक उद्देश्य क्या है?
71.
निम्नलिखित गद्याशं को पढ़कर प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए-
शिक्षा मनुष्य के जीवन का वह दीपक है, जो अज्ञान रूपी अंधकार को दूर करता है और व्यक्ति को सही दिशा में आगे बढ़ने का मार्ग दिखाता है। शिक्षा केवल किताबी ज्ञान नहीं होती, बल्कि यह एक ऐसा साधन है जो व्यक्ति के व्यवहार, सोच और कार्यशैली को सकारात्मक रूप से प्रभावित करती है। प्राचीन भारत में शिक्षा को बहुत ऊँचा स्थान प्राप्त था। गुरुकुलों में विद्यार्थी केवल पाठ्यक्रम ही नहीं पढ़ते थे, बल्कि वे जीवन मूल्यों, मर्यादा, संयम और आत्मनिर्भरता का भी अभ्यास करते थे। आज भले ही शिक्षा पद्धति बदल गई हो, परंतु शिक्षा का उद्देश्य आज भी वही है — एक सच्चे, सजग, और उत्तरदायी नागरिक का निर्माण। शिक्षा व्यक्ति को आत्मविश्वास देती है। एक शिक्षित व्यक्ति समाज की समस्याओं को समझ सकता है, उनके समाधान ढूंढ सकता है और दूसरों को भी जागरूक बना सकता है। शिक्षा ही वह साधन है, जो समाज में व्याप्त रूढ़ियों, अंधविश्वासों और अन्याय के विरुद्ध आवाज़ उठाने की ताकत देता है। महात्मा गाँधी ने कहा था, “वास्तविक शिक्षा वही है जो शरीर, मन और आत्मा — तीनों का समन्वित विकास करे।” इसका तात्पर्य है कि शिक्षा केवल परीक्षा पास करने या नौकरी पाने का माध्यम न होकर एक समग्र व्यक्तित्व निर्माण की प्रक्रिया होनी चाहिए। आज के दौर में डिजिटल शिक्षा, ऑनलाइन कक्षाएं और तकनीकी माध्यमों ने पढ़ाई को आसान बना दिया है, लेकिन इसके साथ ही नैतिक शिक्षा, अनुशासन और मानवीय मूल्यों की शिक्षा भी उतनी ही आवश्यक है। यदि कोई व्यक्ति डिग्रियों से भरा हो लेकिन उसमें सहानुभूति, ईमानदारी और सेवा-भाव न हो, तो वह शिक्षित कहलाने योग्य नहीं। शिक्षा केवल स्कूल या कॉलेज तक सीमित नहीं है। जीवन भर सीखते रहना, नए अनुभवों से ज्ञान प्राप्त करना, गलतियों से सीखना — यह भी शिक्षा का ही एक रूप है। माता-पिता, शिक्षक, समाज और स्वयं जीवन — सभी शिक्षा के स्रोत हैं। एक शिक्षित समाज ही प्रगति कर सकता है। शिक्षा ही वह नींव है जिस पर एक सशक्त राष्ट्र का निर्माण होता है। इसलिए यह हम सभी का कर्तव्य है कि हम स्वयं भी शिक्षा प्राप्त करें और दूसरों को भी शिक्षित करने में सहयोग दें। विशेषकर बालिकाओं और वंचित वर्ग के बच्चों को शिक्षा का अवसर प्रदान करना समाज की सच्ची सेवा है। इस प्रकार, शिक्षा वह अमूल्य धन है जिसे कोई चुरा नहीं सकता, कोई बांध नहीं सकता और जो जितना बांटें, उतना ही बढ़ता है। यही शिक्षा की सबसे बड़ी विशेषता है।
प्रश्न 1.प्राचीन भारत में शिक्षा किस प्रकार दी जाती थी?
72.
निम्नलिखित गद्याशं को पढ़कर प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए-
शिक्षा मनुष्य के जीवन का वह दीपक है, जो अज्ञान रूपी अंधकार को दूर करता है और व्यक्ति को सही दिशा में आगे बढ़ने का मार्ग दिखाता है। शिक्षा केवल किताबी ज्ञान नहीं होती, बल्कि यह एक ऐसा साधन है जो व्यक्ति के व्यवहार, सोच और कार्यशैली को सकारात्मक रूप से प्रभावित करती है। प्राचीन भारत में शिक्षा को बहुत ऊँचा स्थान प्राप्त था। गुरुकुलों में विद्यार्थी केवल पाठ्यक्रम ही नहीं पढ़ते थे, बल्कि वे जीवन मूल्यों, मर्यादा, संयम और आत्मनिर्भरता का भी अभ्यास करते थे। आज भले ही शिक्षा पद्धति बदल गई हो, परंतु शिक्षा का उद्देश्य आज भी वही है — एक सच्चे, सजग, और उत्तरदायी नागरिक का निर्माण। शिक्षा व्यक्ति को आत्मविश्वास देती है। एक शिक्षित व्यक्ति समाज की समस्याओं को समझ सकता है, उनके समाधान ढूंढ सकता है और दूसरों को भी जागरूक बना सकता है। शिक्षा ही वह साधन है, जो समाज में व्याप्त रूढ़ियों, अंधविश्वासों और अन्याय के विरुद्ध आवाज़ उठाने की ताकत देता है। महात्मा गाँधी ने कहा था, “वास्तविक शिक्षा वही है जो शरीर, मन और आत्मा — तीनों का समन्वित विकास करे।” इसका तात्पर्य है कि शिक्षा केवल परीक्षा पास करने या नौकरी पाने का माध्यम न होकर एक समग्र व्यक्तित्व निर्माण की प्रक्रिया होनी चाहिए। आज के दौर में डिजिटल शिक्षा, ऑनलाइन कक्षाएं और तकनीकी माध्यमों ने पढ़ाई को आसान बना दिया है, लेकिन इसके साथ ही नैतिक शिक्षा, अनुशासन और मानवीय मूल्यों की शिक्षा भी उतनी ही आवश्यक है। यदि कोई व्यक्ति डिग्रियों से भरा हो लेकिन उसमें सहानुभूति, ईमानदारी और सेवा-भाव न हो, तो वह शिक्षित कहलाने योग्य नहीं। शिक्षा केवल स्कूल या कॉलेज तक सीमित नहीं है। जीवन भर सीखते रहना, नए अनुभवों से ज्ञान प्राप्त करना, गलतियों से सीखना — यह भी शिक्षा का ही एक रूप है। माता-पिता, शिक्षक, समाज और स्वयं जीवन — सभी शिक्षा के स्रोत हैं। एक शिक्षित समाज ही प्रगति कर सकता है। शिक्षा ही वह नींव है जिस पर एक सशक्त राष्ट्र का निर्माण होता है। इसलिए यह हम सभी का कर्तव्य है कि हम स्वयं भी शिक्षा प्राप्त करें और दूसरों को भी शिक्षित करने में सहयोग दें। विशेषकर बालिकाओं और वंचित वर्ग के बच्चों को शिक्षा का अवसर प्रदान करना समाज की सच्ची सेवा है। इस प्रकार, शिक्षा वह अमूल्य धन है जिसे कोई चुरा नहीं सकता, कोई बांध नहीं सकता और जो जितना बांटें, उतना ही बढ़ता है। यही शिक्षा की सबसे बड़ी विशेषता है।
प्रश्न 1. महात्मा गाँधी के अनुसार वास्तविक शिक्षा किसका विकास करती है?
73.
निम्नलिखित गद्याशं को पढ़कर प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए-
शिक्षा मनुष्य के जीवन का वह दीपक है, जो अज्ञान रूपी अंधकार को दूर करता है और व्यक्ति को सही दिशा में आगे बढ़ने का मार्ग दिखाता है। शिक्षा केवल किताबी ज्ञान नहीं होती, बल्कि यह एक ऐसा साधन है जो व्यक्ति के व्यवहार, सोच और कार्यशैली को सकारात्मक रूप से प्रभावित करती है। प्राचीन भारत में शिक्षा को बहुत ऊँचा स्थान प्राप्त था। गुरुकुलों में विद्यार्थी केवल पाठ्यक्रम ही नहीं पढ़ते थे, बल्कि वे जीवन मूल्यों, मर्यादा, संयम और आत्मनिर्भरता का भी अभ्यास करते थे। आज भले ही शिक्षा पद्धति बदल गई हो, परंतु शिक्षा का उद्देश्य आज भी वही है — एक सच्चे, सजग, और उत्तरदायी नागरिक का निर्माण। शिक्षा व्यक्ति को आत्मविश्वास देती है। एक शिक्षित व्यक्ति समाज की समस्याओं को समझ सकता है, उनके समाधान ढूंढ सकता है और दूसरों को भी जागरूक बना सकता है। शिक्षा ही वह साधन है, जो समाज में व्याप्त रूढ़ियों, अंधविश्वासों और अन्याय के विरुद्ध आवाज़ उठाने की ताकत देता है। महात्मा गाँधी ने कहा था, “वास्तविक शिक्षा वही है जो शरीर, मन और आत्मा — तीनों का समन्वित विकास करे।” इसका तात्पर्य है कि शिक्षा केवल परीक्षा पास करने या नौकरी पाने का माध्यम न होकर एक समग्र व्यक्तित्व निर्माण की प्रक्रिया होनी चाहिए। आज के दौर में डिजिटल शिक्षा, ऑनलाइन कक्षाएं और तकनीकी माध्यमों ने पढ़ाई को आसान बना दिया है, लेकिन इसके साथ ही नैतिक शिक्षा, अनुशासन और मानवीय मूल्यों की शिक्षा भी उतनी ही आवश्यक है। यदि कोई व्यक्ति डिग्रियों से भरा हो लेकिन उसमें सहानुभूति, ईमानदारी और सेवा-भाव न हो, तो वह शिक्षित कहलाने योग्य नहीं। शिक्षा केवल स्कूल या कॉलेज तक सीमित नहीं है। जीवन भर सीखते रहना, नए अनुभवों से ज्ञान प्राप्त करना, गलतियों से सीखना — यह भी शिक्षा का ही एक रूप है। माता-पिता, शिक्षक, समाज और स्वयं जीवन — सभी शिक्षा के स्रोत हैं। एक शिक्षित समाज ही प्रगति कर सकता है। शिक्षा ही वह नींव है जिस पर एक सशक्त राष्ट्र का निर्माण होता है। इसलिए यह हम सभी का कर्तव्य है कि हम स्वयं भी शिक्षा प्राप्त करें और दूसरों को भी शिक्षित करने में सहयोग दें। विशेषकर बालिकाओं और वंचित वर्ग के बच्चों को शिक्षा का अवसर प्रदान करना समाज की सच्ची सेवा है। इस प्रकार, शिक्षा वह अमूल्य धन है जिसे कोई चुरा नहीं सकता, कोई बांध नहीं सकता और जो जितना बांटें, उतना ही बढ़ता है। यही शिक्षा की सबसे बड़ी विशेषता है।
प्रश्न 1.शिक्षित समाज की मुख्य विशेषता क्या होती है?
74.
निम्नलिखित गद्याशं को पढ़कर प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए-
शिक्षा मनुष्य के जीवन का वह दीपक है, जो अज्ञान रूपी अंधकार को दूर करता है और व्यक्ति को सही दिशा में आगे बढ़ने का मार्ग दिखाता है। शिक्षा केवल किताबी ज्ञान नहीं होती, बल्कि यह एक ऐसा साधन है जो व्यक्ति के व्यवहार, सोच और कार्यशैली को सकारात्मक रूप से प्रभावित करती है। प्राचीन भारत में शिक्षा को बहुत ऊँचा स्थान प्राप्त था। गुरुकुलों में विद्यार्थी केवल पाठ्यक्रम ही नहीं पढ़ते थे, बल्कि वे जीवन मूल्यों, मर्यादा, संयम और आत्मनिर्भरता का भी अभ्यास करते थे। आज भले ही शिक्षा पद्धति बदल गई हो, परंतु शिक्षा का उद्देश्य आज भी वही है — एक सच्चे, सजग, और उत्तरदायी नागरिक का निर्माण। शिक्षा व्यक्ति को आत्मविश्वास देती है। एक शिक्षित व्यक्ति समाज की समस्याओं को समझ सकता है, उनके समाधान ढूंढ सकता है और दूसरों को भी जागरूक बना सकता है। शिक्षा ही वह साधन है, जो समाज में व्याप्त रूढ़ियों, अंधविश्वासों और अन्याय के विरुद्ध आवाज़ उठाने की ताकत देता है। महात्मा गाँधी ने कहा था, “वास्तविक शिक्षा वही है जो शरीर, मन और आत्मा — तीनों का समन्वित विकास करे।” इसका तात्पर्य है कि शिक्षा केवल परीक्षा पास करने या नौकरी पाने का माध्यम न होकर एक समग्र व्यक्तित्व निर्माण की प्रक्रिया होनी चाहिए। आज के दौर में डिजिटल शिक्षा, ऑनलाइन कक्षाएं और तकनीकी माध्यमों ने पढ़ाई को आसान बना दिया है, लेकिन इसके साथ ही नैतिक शिक्षा, अनुशासन और मानवीय मूल्यों की शिक्षा भी उतनी ही आवश्यक है। यदि कोई व्यक्ति डिग्रियों से भरा हो लेकिन उसमें सहानुभूति, ईमानदारी और सेवा-भाव न हो, तो वह शिक्षित कहलाने योग्य नहीं। शिक्षा केवल स्कूल या कॉलेज तक सीमित नहीं है। जीवन भर सीखते रहना, नए अनुभवों से ज्ञान प्राप्त करना, गलतियों से सीखना — यह भी शिक्षा का ही एक रूप है। माता-पिता, शिक्षक, समाज और स्वयं जीवन — सभी शिक्षा के स्रोत हैं। एक शिक्षित समाज ही प्रगति कर सकता है। शिक्षा ही वह नींव है जिस पर एक सशक्त राष्ट्र का निर्माण होता है। इसलिए यह हम सभी का कर्तव्य है कि हम स्वयं भी शिक्षा प्राप्त करें और दूसरों को भी शिक्षित करने में सहयोग दें। विशेषकर बालिकाओं और वंचित वर्ग के बच्चों को शिक्षा का अवसर प्रदान करना समाज की सच्ची सेवा है। इस प्रकार, शिक्षा वह अमूल्य धन है जिसे कोई चुरा नहीं सकता, कोई बांध नहीं सकता और जो जितना बांटें, उतना ही बढ़ता है। यही शिक्षा की सबसे बड़ी विशेषता है।
प्रश्न 1. निम्न में से कौन-सी बात शिक्षा की विशेषता नहीं है?
75.
Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and so form a group.
Which is the one that does not belong to that group?
JNR, DHL, CGK, EIM, FKP
76.
Select the next number in the series.
77.
In a certain code language, ‘BUZZY’ is coded as ’10’ and ‘KING’ is coded as ‘8’. How will ‘ABROAD’ be coded in the same language?
78.
Two different positions of the same dice are given below. What is the number on the face opposite to the face with number 1?
79.
Seema goes 45 m in the north-west direction from her uncle's house. She meets her friend and goes 45 m in the south-west direction. Then she goes 45 m in the south-east. And turns left and walks towards uncle's house. In which direction is she going now?
80.
Read the given statements and conclusions carefully. Assuming that the information given in the statements is true, even if it seems to be at variance with commonly known facts, decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the statements.
Statements:
Some stars are planets.
All stars are comets.
Conclusions:
I. Some comets are planets.
II. Some planets are stars.
81.
How many squares are there in the given figure?
82.
Six letters A, B, C, P, Q and R are written on different faces of a dice. Two positions of this dice are shown in the given figure. Which letter is on the face opposite to the face with the letter C?
83.
From the given option figures, select the figure which when placed at the place of question mark (?) in the figure given below will complete the pattern.
84.
In a code language, if MUSIC is coded as 13 – 21- 19- 9 – 3 and BAND is coded as 2 – 1 – 14 – 4, then how will HARMONIUM be coded?
85.
If A stands for '+', B stands for '\(\times\), C stands for '-', and D stands for '\(\div\)', then what will come in place of '?' in the following equation?
24 D (1 A 7) C 2 A 7 B 12 B (5 C 4) = ?
86.
Select the number from the given options that can replace the question mark (?) in the following series?
87.
N is the brother of Y and Y is the sister of B. B is the wife of Z and C is the mother of Y. How is Z related to C?
88.
In a certain code language, ‘DO’ is written as ’60’, ‘PIE’ is written as ‘720’. How will ‘CAT’ be written in that code language?
89.
Select the option that has the same relation with the third number as the second number has with the first number.
90.
In a certain code language ROME is written as VSQI. Which word will be written as RMGI in the same code language?
91.
Select the figure from the given options that will come in place of question mark (?) to logically complete the following series.
92.
In a certain code language, 'green colour is my favourite' is coded as 'ni li pi si fu' and 'trees are dark green' is coded as 'ai pi bi ii'. How is 'green' coded in the given language?
93.
Seven students Q, R, S T, W, X and Y are sitting in a straight row facing north. No one is sitting to the left of R. X is sitting to the immediate left of S. Only four students are sitting between R and T. Only three students are sitting to the right of Y. W is not the immediate neighbour of Y. How many students are sitting between W and Y?
94.
All 51 students in a class are standing in a row facing north. Aditi is 21st from the right end while Sagar is 35th from the left end. How many students are standing between Aditi and Sagar?
95.
Find the related word.
Surgeon : Knife :: Carpenter : ?
96.
Find the missing numbers (A and B) in the series and find the value of B – A.
11, 22, 33, A, 55, 66, 77, B
97.
Find the next number in the series 1, 6, 23, 76,__________.
98.
Find the different words.
99.
Find the missing numbers 1, 12, 144, …………, 20736.
100.
Refer to the following number and symbol series and answer the given question. Counting is to be done from left to right only.
(left) & / 7 5 6 / < @ * 6 @ 8 3 9 & ^ 6 (right)
How many such symbols are there, each of which is immediately preceded by a number and immediately followed by a number?
101.
Select the combination of letters that when sequentially placed in the blanks of the given series will complete the series.
DB_ A H_GE_JKI PN _ M T _ SQ
102.
If 'A' means '\(\div\), 'B' means '\(\times\)', 'C' means '+' and 'D' means '-', then what will come in place of question mark (?) in the following equation?
103.
Select the triplet that follows the same pattern as the given two triplets. Both the triplets follow the same pattern.
104.
Which of the following letter – number cluster will replace the question mark (?) to make the given series logically complete?
AFC18 DIF27 GLI36 JOL45 ?
105.
Rahul is the husband of Antima. Dev is the brother of Kusha. Shalini is the mother of Kusha's mother. Dev is the son of Rahul. How is Antima related to Shalini?
106.
Which of the following letter – number cluster should replace the question mark (?) in the given series in order to make it logically complete?
CO 72, KI 76, SC 82, AW 90, ?
107.
If '+' means '-', '-' means '\(\times\)', '\(\times\)' means '\(\div\) and \(\div\)' means '+', then what will come in place of '(?)' in the following equation?
\(36 – 5 \div 240 \times 6 + 17 = ?\)
108.
Three of the following letter-clusters are alike in some way, and one is alike. Choose the alike letter-cluster.
109.
Select the option that represents the letters that when placed sequentially from left to right in the blanks given below will complete the given letter series.
P _ _ H _ _ C E _ Z P _ E H _
110.
Which of the following letter-cluster will come in place of the question mark (?) in the given series and complete the series?
VQSN, ?, ROOL, PNMK, NMKJ
111.
Which of the following numbers will replace the question mark (?) in the given series?
352, 326, 284, 225, 148, ?
112.
A man is standing in a park facing north. He turns \(90^\circ\) left and walks 40 Km. He again turns \(90^\circ\) right and walks 50 km. He again turns \(90^\circ\) right and walks 60 km. Finally, he turns \(90^\circ\) right and walks 50 km. How far is he from the starting point?
113.
A 375 m long train passes a man travelling in the opposite direction at a speed of 10.2 km/h in 15 seconds. Find the speed of the train (in km/h).
114.
A pipe can fill a tank in 7 hours. Another pipe can empty the full tank in 21 hours. If both the pipes are opened simultaneously, then how much time (in hours) will it take to fill two-thirds of the tank?
115.
Find the Greatest Common Factor (HCF) of 24 and 36.
116.
A wholesaler sells a tin of soybean oil for ₹5,720 and incurs a loss of 12%. Now, if he decides to sell the second tin of soybean oil for ₹7,475, find his profit percentage in the sale of the second tin.
117.
The sum of five numbers is 655. The average of the first two numbers is 77 and the third number is 132. Find the average of the remaining two numbers.
118.
A car travels 194 Km in the first hour and 286 km in the second hour. Completes the journey. Find the average speed (in km/h) of the car during the entire journey.
119.
A trader marks his goods 30% more than the cost price and gives his customers a discount of 20% on their bills. What percentage of profit does he make?
120.
Find the volume of a cube whose diagonal length is \(18\sqrt{3}\) cm.
121.
In what ratio should sugar costing ₹ 27 per kg be mixed with sugar costing ₹ 55 per kg so that a profit of 44% is made by selling the mixture at ₹ 57.6 per kg?
122.
After pouring 57 litres of petrol into an empty storage tank, it still remains 1% empty. How much petrol (in litres, rounded off to two decimal places) must be poured into the storage tank to fill it?
123.
Find the value of \(\frac{3.6\times 0.48 \times 2.50}{0.12\times 0.09\times0.5}\).
124.
If you lend ₹4,000 to your friend for 2 years at 5% annual compound interest rate, then how much amount (in ₹) will your friend return after 2 years?
125.
What is the smallest number which on subtracting 9 from it becomes divisible by 24, 33, 42 and 56?
126.
The sum of 8 numbers is 720. Find their average.
127.
Let O be the centre of the circle and AB and CD are two parallel chords of equal side of radius 1. OP is perpendicular to AB and OQ is perpendicular to CD. If AB = 10 cm., CD = 24 cm and PQ = 7 cm, then the diameter (in cm) of the circle is _________.
128.
If the sum of two sides of an equilateral triangle is 16 cm, find the third side.
129.
The ratio of milk and water in 90 liters of a mixture is 4 : 1. The ratio of milk and water in 90 liters of another mixture is 3 : 2. Find the positive difference between the quantities of milk in the two mixtures.
130.
Which of the following numbers is divisible by 30?
131.
In the set of data given below, find the difference between the median and mode:
{2.1, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.3, 11, 15, 17, 19.21, 27, 31, 31, 33, 16.5, 14, 10}
132.
A train covers a distance of 57.6 km in 48 minutes. Find its speed in m/s.
133.
A can complete 12% of a piece of work in 15% of the prescribed time. A and B work for the full duration of the prescribed time, and the work is completed on time. What part of the work does B complete?
134.
Find the smallest cube number which is divisible by 72, 108 and 300?
135.
If 15% of A : 25% of B :: 8 : 11, then A : B is equal to ___________.
136.
A person travels from Kolkata to Ahmedabad at a speed of 9km/hr and returns back to Kolkata by the same route at a speed of 18 km/hr. Find his average speed (in km/hr) during the entire journey.
137.
The LCM and HCF of two numbers are 144 and 8 respectively. If one of the numbers is 16, find the other number.
138.
Ram, Ravi and Reena can complete a piece of work in 16, 20 and 24 days respectively. They started the work together but Ravi left 5 days before the completion of the work. In how many days did the other two together complete the work?
139.
Kanchan sold 153 chairs and made a profit equal to the selling price of 78 chairs. What is her profit percentage?
140.
Find the least common multiple (LCM) of 30, 13, 180, and 234.
141.
The product of two numbers is 1,48,176 and the value of their LCM is 3,528. Find their HCF.
142.
The average age of 22 students of a class is 47 years. If the age of the teacher is also included, then the average age of the entire group becomes 48 years. Find the age of the teacher (in years).
143.
At the same rate of simple interest per annum, Gopal invests an amount of ₹5400 and Akshay invests an amount of ₹10200. If at the end of 4 years, Akshay gets ₹720 more interest than Gopal, then find the rate of interest per annum (in percentage).
144.
Find the number that can be subtracted from both terms of the ratio 43 : 91 so that the ratio becomes 3 : 7.
145.
If the difference between compound interest and simple interest for three years at 10% annual interest rate is ₹93, then find the principal (in ₹).
146.
Find the value of the following.
\([(16 \times 12) \times \{ 5 \div 5\times \frac{(13 -11)}{2}\}]\)
147.
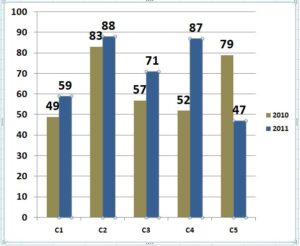
Study the following bar graph and answer the following question.
Sales of books (in thousands) from 5 branches (C 1, C 2, C 3, C 4 and C 5) of a publishing company for two consecutive years 2010 and 2011. What is the average sales of all the branches (in thousands) in the year 2010?
148.
The total area of a piece of square glass is 784 cm \(^2\), which is placed on top of a table. The width between the edge of the table and the piece of glass is 9 cm wide. Find the length of the table.
149.
When a number is divided by 84, the remainder is 10. What will be the remainder when that number is divided by 12?
150.
Simplify
\(196^2\times 56 \div 14^5 \times 1021\) = ?
Leave a Reply